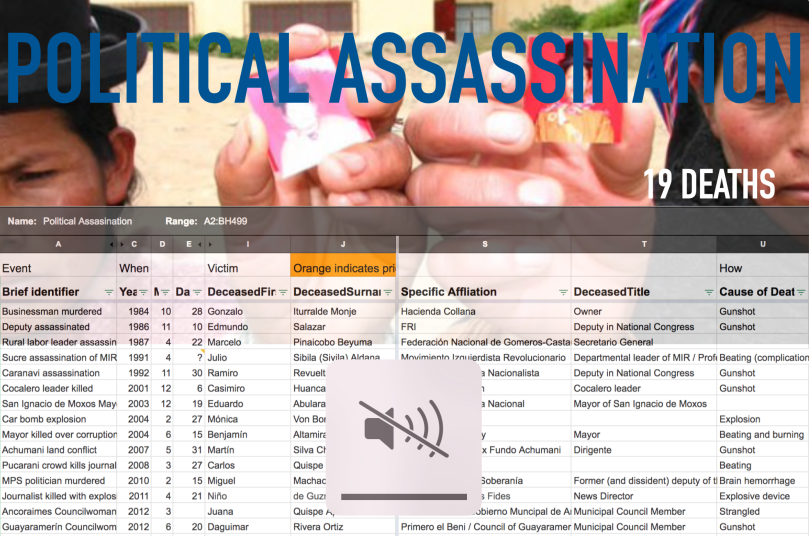
This presentation introduces Ultimate Consequences, a quantitative and qualitative database, unique in its depth and completeness of coverage, of all conflict deaths in Bolivia since October 1982, a period of largely elected governments and political dynamism. The country’s 1977–82 return to democracy, 1985 general strikes, 2000–2005 antineoliberal protest wave, and its political crises in 2006–2008 and 2019–2020 each exemplify the ability of mass disruptive protest to remake national politics. The database enables comparative analysis across twelve presidential administrations, four episodes where protesters successfully sought the end of a presidential term, and 192 protest events in 17 domains of conflict. Due to the number of lethal events in the study period, the dataset is both large enough for quantitative research that analyzes patterns and small enough for qualitative, journalistic, and historical examination of the individual deaths involved. To serve these multiple purposes, we are coding information such as individuals’ relation to a specific social movement, protest campaign, cause of death, responsible parties, and location, and writing detailed narrative descriptions about major events. The presentation introduces the open data format of the database and the R-based tools to explore it.
The project draws on journalistic, advocacy, and scholarly sources to comprehensively document all deaths in political conflict, including those not readily categorizable as human rights violations. The project also seeks to ask more intimate, and cultural, questions about the role of risk, violence, sacrifice, and loss in transformative social change. As the database reveals, Bolivian protest can involve intense risk, privation, self-sacrifice, and either enduring or inflicting violence. Bolivian social movement traditions include proclamations of fearlessness and vows to carry on their struggles “until the ultimate consequences,” that is, to persist in collective measures and to refuse to be deterred by deadly state violence. These movements invoke a history of indigenous uprisings, labor militancy, and state massacres in narrating their own histories.
The dataset offers a grounded view on such questions as: What practices and political choices result in some presidencies being far less violent than others? What is the relative importance of different forms of political violence, from repression of protest to guerrilla movements to fratricidal disputes among movements? Which movements have succeeded despite deadly repression? This presentation introduces a new tool for social scientists, oral historians, and human rights advocates to use in answering these and other questions.